Complete Blood Count (CBC) is also known as Full Body Count (FBC). CBC is a common blood test that measures various components of your blood. It’s a widely used and essential medical tool that provides valuable information about your overall health.
Here is detail information on each Components of CBC profile:
HAEMOGLOBIN (HB):
- What is Haemoglobin?
Hemoglobin, also spelled haemoglobin, is a protein found in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. It’s a crucial component of the respiratory system, enabling the transportation of oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs.
Here’s detail information of hemoglobin and their vital role:
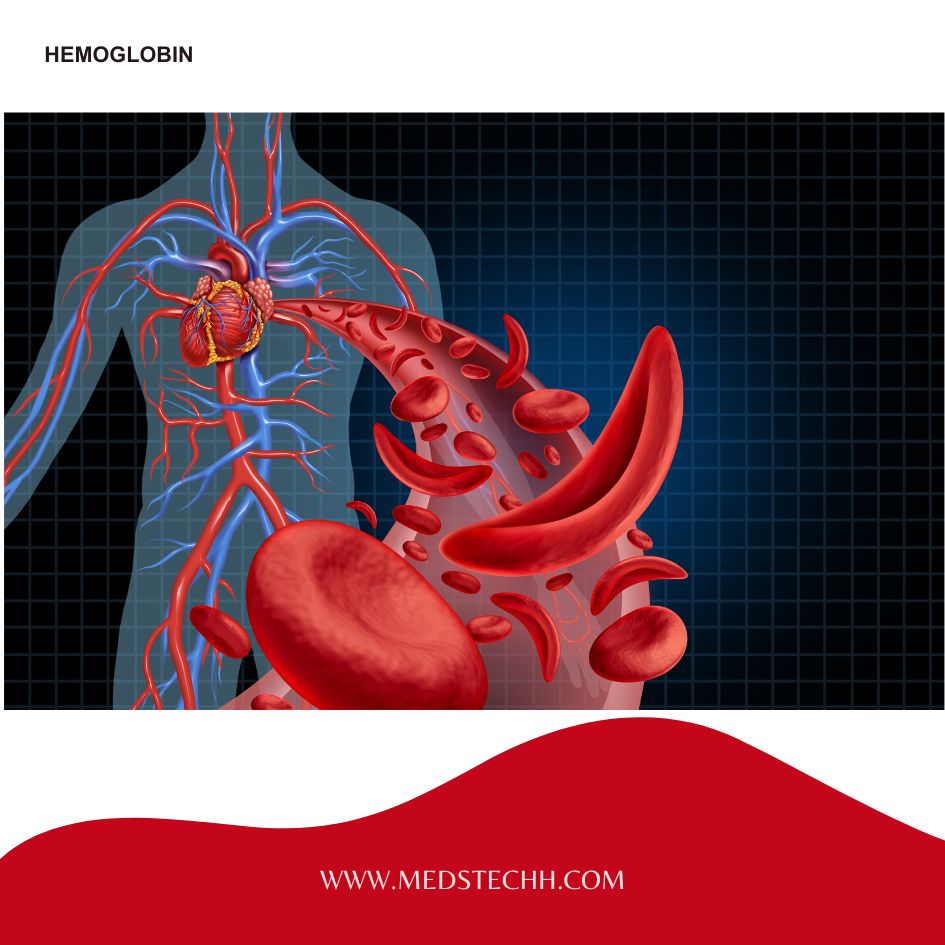
- What is structure hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a complex molecule composed of protein chains and iron-containing heme groups. The iron within the heme group binds to oxygen, allowing hemoglobin to carry multiple oxygen molecules at once.
- What is function hemoglobin?
When red blood cells pass through the lungs, oxygen readily binds to hemoglobin due to the high concentration of oxygen in the alveoli (air sacs). As the blood circulates through the body, oxygen is released from hemoglobin in areas with lower oxygen levels, delivering oxygen to tissues and organs that require it for various functions.
- Importance of hemoglobin in your body.
Hemoglobin plays a vital role in maintaining proper oxygen supply to the body’s cells. Adequate levels of hemoglobin are essential for various physiological processes, including energy production, growth, and repair.
RED BLOOD CELLS (R.B.C.s):
- What is Red Blood Cell (R.B.C)?
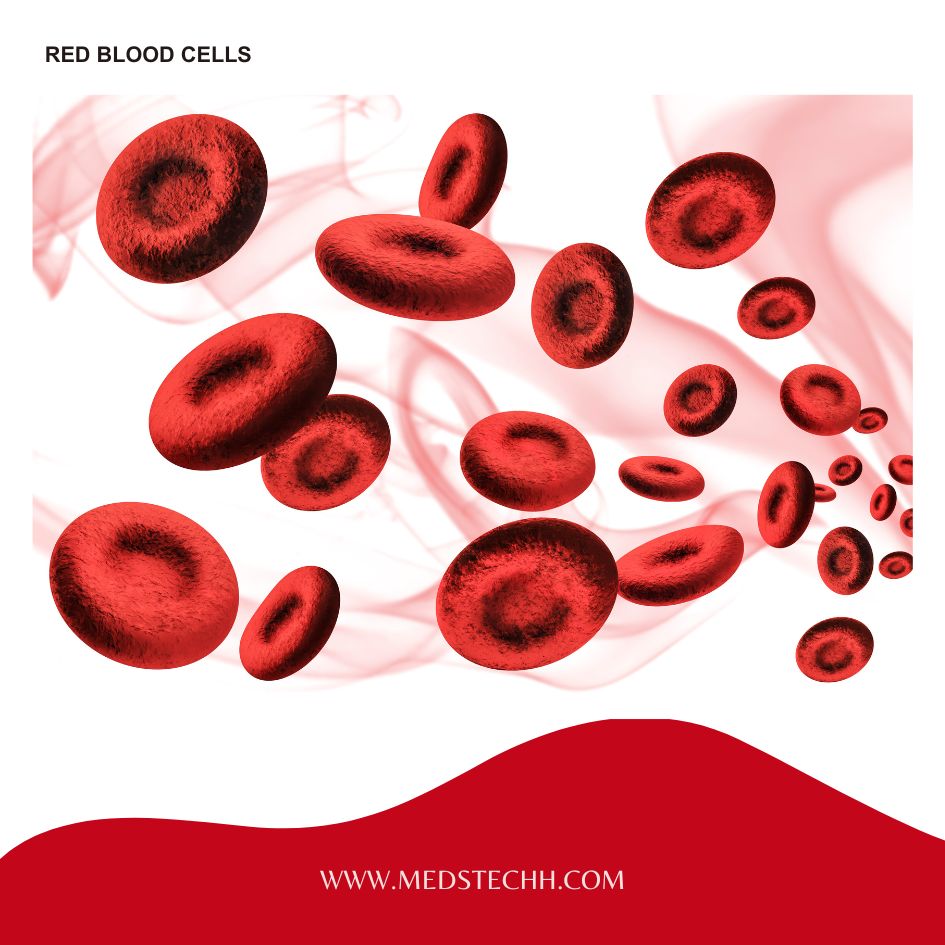
Red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are tiny disc-shaped cells found in vast numbers within your blood. They are the primary delivery service for a critical element in your body: OXYGEN. These cells carry oxygen throughout your body. The CBC measures the number of RBCs, their size, and the amount of hemoglobin they contain.
Here’s detail information of Red Blood Cells and their vital role:
- What is Function of Red Blood Cell (R.B.C)?
Oxygen Transport: Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which is the key player in oxygen delivery. Hemoglobin has iron at its core, which binds readily with oxygen molecules inhaled from your lungs.
- Delivering Oxygen Throughout the Body: Once loaded with oxygen, red blood cells travel through your bloodstream, squeezing through tiny capillaries to reach every nook and cranny of your body.
- Carbon Dioxide Removal: Red blood cells don’t just deliver; they also pick up waste. Red blood cells capture this carbon dioxide and transport it back to your lungs for exhalation.
- Importance of Red Blood Cells in your body.
- Cellular Energy Production: Every cell in your body relies on oxygen for energy production. Without a steady supply from red blood cells, your organs, muscles, and even your brain wouldn’t function properly.
- Maintaining Vital Functions: Oxygen is essential for all your body’s processes, from thinking clearly and maintaining a healthy metabolism to keeping your heart beating and your immune system strong.
- Overall Health: A healthy red blood cell count is vital for overall well-being. It ensures your body has the fuel it needs to function optimally and maintain a strong defense against illness.
More Components of R.B.C.s:
- Red blood cell count (RBC): This measures the number of red blood cells per micro liter of blood.
- Hematocrit (HCT): This is the percentage of your blood volume that is made up of red blood cells.
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): This is the average size of your R.B.C.s.
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH): This is the average amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell.
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC): This is the concentration of hemoglobin in your red blood cells.
WHITE BLOOD CELL COUNT (W.B.C):
- What is white blood cell (W.B.C)?
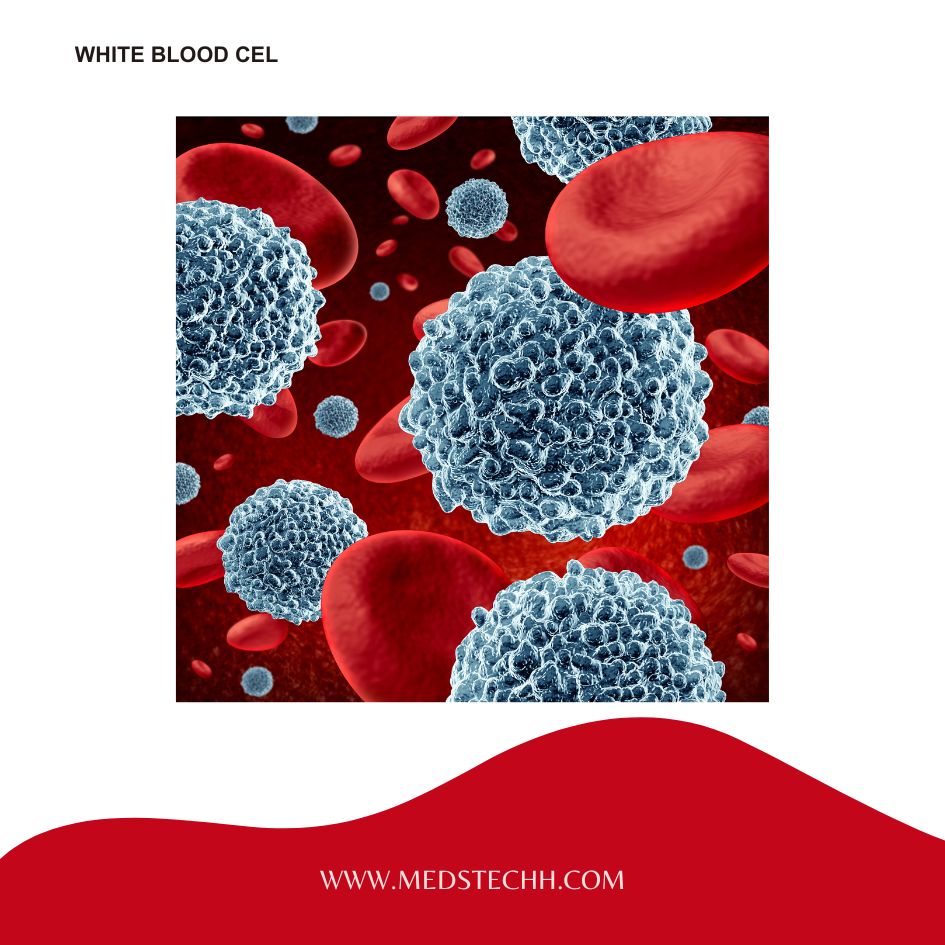
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are a crucial part of your body’s defense system, the immune system. They act as the army that protects you from invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause illness.
Here’s why White Blood Cells are essential for human health and their vital role:
- Infection Fighters: White blood cells constantly patrol your bloodstream and tissues, searching for anything foreign or harmful. They can directly engulf and destroy these invaders, like neutrophils do with bacteria.
- Immune Response: Some white blood cells, like lymphocytes, produce specialized proteins called antibodies that target specific pathogens. These antibodies latch onto the invaders, making them easier for other white blood cells to destroy.
- Inflammation Management: When white blood cells detect an infection, they trigger inflammation, a process that brings more immune cells to the area to fight the threat.
- Disease Prevention: White blood cells also play a role in preventing diseases like cancer. They can identify and eliminate abnormal cells before they multiply and cause harm.
Components and Types of W.B.C.s:
- WBC differential: There are several different types of white blood cells, each with a specific function:
- Neutrophils: These are the most abundant white blood cells and the first line of defense against bacteria.
- Lymphocytes: These cells produce antibodies and are essential for long-term immunity.
- Monocytes: These cells mature into macrophages, which engulf and digest debris, including bacteria and dead cells.
- Eosinophils: These cells are involved in allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
- Basophils: These cells are less common and their exact function is still being studied, but they seem to be involved in allergic reactions and inflammation.
- These cells are part of your immune system and help fight infection. The CBC measures the total number of WBCs and the percentage of each type of WBC.
PLATELETS:
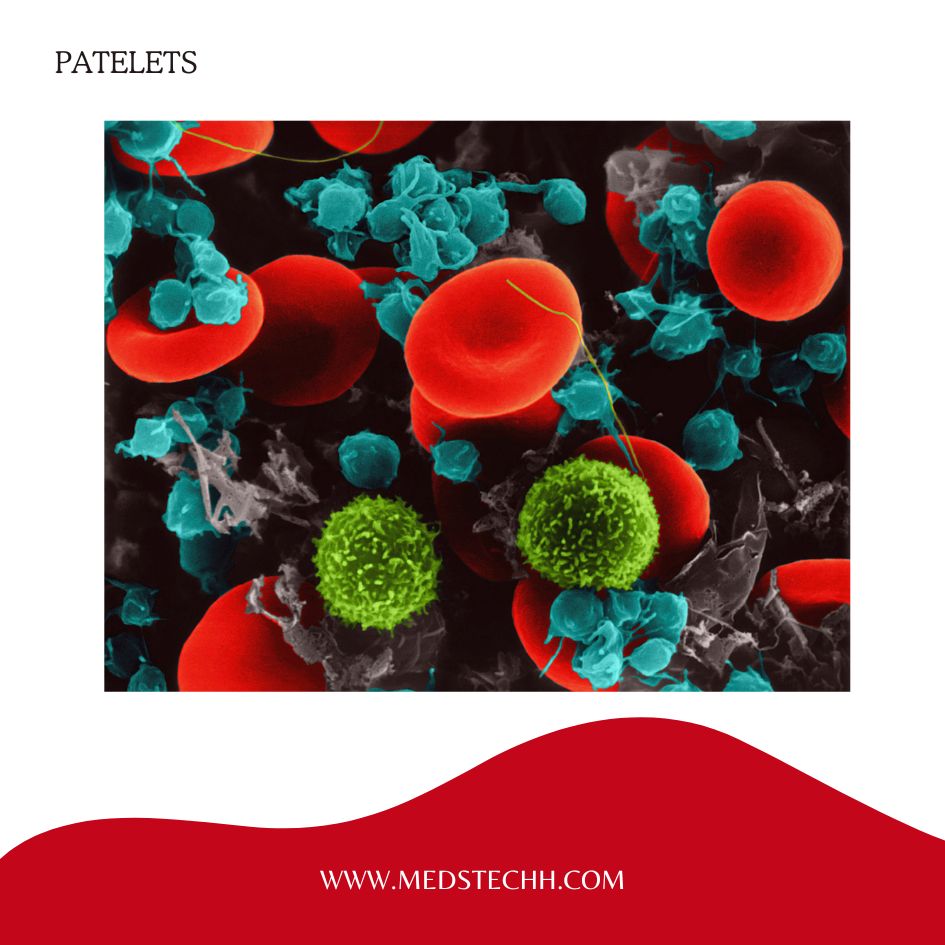
- What is Platelets?
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are tiny, colorless cell fragments found in your blood. Platelets are non-nucleated cell elements; they play a crucial role in the body’s clotting system and stop bleeding.
Here’s why Platelets are essential for human health and their vital role:
- Prevent and Stop Bleeding: Their primary function is to control bleeding by forming clots at the site of injury. When a blood vessel is damaged, platelets rush to the area and clump together to form a plug, sealing the leak and preventing excessive blood loss.
- Wound Healing: Platelets also release chemicals that attract other clotting factors and promote wound healing. They contribute to the overall healing process by stimulating the growth of new tissue.
- Maintaining Blood Vessel Integrity: Platelets interact with the lining of blood vessels to maintain their integrity and prevent unnecessary clotting within the circulatory system.
Maintaining a healthy platelet count is essential for proper blood clotting and preventing excessive bleeding or clotting complications. A normal platelet count generally falls within the range of 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per micro liter of blood.
More components of Platelet:
- Mean platelet volume (MPV): This is the average size of your platelets.
- Platelet distribution width (PDW): This measures the variation in the size of your platelets.
- Plateletcrit (PCT): This is the percentage of your blood volume that is made up of platelets.
- Large platelet count (LPL): This measures the number of large platelets in your blood.
- Mean platelet component ratio (MCR): This is the ratio of the mean platelet volume to the MCV.
IMPORTANCE OF CBC/FBC TEST:
A CBC test is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of medical conditions, including:
- Anemia: A condition in which you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout your body.
- Infection: An increase in white blood cells can indicate an infection.
- Bleeding disorders: A low platelet count or abnormal platelet function can increase your risk of bleeding.
- Leukemia: White blood cells Cancer.
- Other conditions: A CBC can also help identify other conditions, such as malnutrition, inflammation, and autoimmune diseases.
CBC is a routine part of many physical exams and can also be ordered if you have specific symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, or easy bruising
- CBC/FBC FULL PROFILE AND NORMAL VALUES.
| Test | Reference Values |
| Haemoglobin | Male: 13 – 17 gm/dL Female: 12 – 15 gm/dL New Born: 14 – 22 gm/dL Upto 1 Month: 12.5 – 16.5 gm/dL 3 Months – 6 Years: 11 – 14 gm/dL |
| W.B.C.s | 02 Months-2 Years: 5,000-15,000/ µl Adult: 4,000 – 10,000/ µl |
| Neutrophils | 40 – 80 % |
| Lymphocytes | 20 – 40 % |
| Monocytes | 2 – 10 % |
| Eosinophils | 01 – 06 % |
| Platelet Count | 1,50,000 – 4,10,000 / µl |
| R.B.C.s | Male: 4.5 – 5.5 millions/ µl Female: 3.8 – 4.8 millions/ µl |
| HCT. | Male: 40 – 50 % Female: 36 – 46 % |
| M.C.V. | 76 – 96 fL |
| M.C.H. | 27 – 32 pg |
| M.C.H.C. | 31.5 – 34.5 gm/dL |




Hello, I have a question
Yes, what is your question?
Greetings from Ohio! I’m bored at work so I decided to check out your website on my iphone during lunch break. I love the info you provide here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, very good blog!
I don抰 even know the way I ended up here, but I assumed this put up was once good. I do not realize who you’re but certainly you are going to a famous blogger in the event you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I have been browsing on-line more than 3 hours these days, yet I by no means discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is pretty value enough for me. In my opinion, if all webmasters and bloggers made just right content as you did, the internet might be much more useful than ever before.
As I website possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling fantastic , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
Impressive efforts