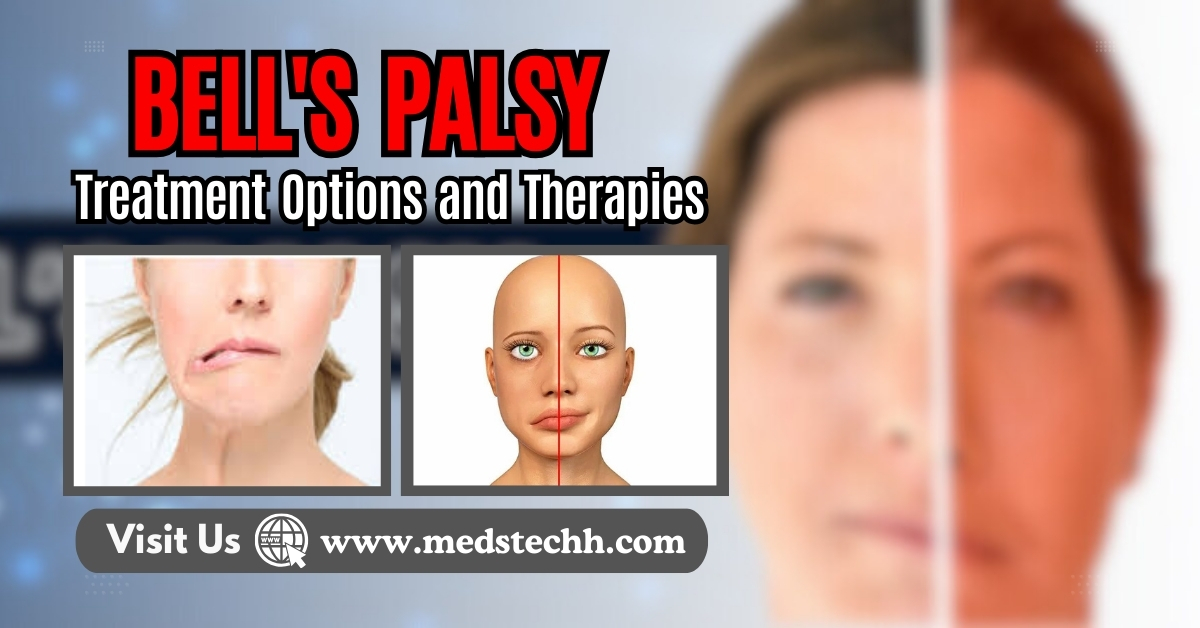
Introduction:
Bell’s Palsy is also known as Facial Palsy. Bell’s Palsy is a condition that affects facial muscles, leading to temporary weakness or paralysis on one side of the face. It occurs when the seventh cranial nerve, known as the facial nerve, becomes inflamed or compressed, resulting in facial drooping and other symptoms. Comprehensive information about Bell’s Palsy, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recommended exercises for recovery.
Causes of Bell’s Palsy
Viral Infections:
The precise cause of Bell’s Palsy is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. These include viral infections, particularly herpes simplex virus (HSV), which is responsible for cold sores and genital herpes. Other viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV), have also been linked to Bell’s Palsy.
Nerve Inflammation:
Inflammation of the facial nerve can disrupt its function, leading to the characteristic symptoms of Bell’s Palsy. The exact cause of nerve inflammation is not always clear, but it is believed to be related to viral infections, immune system responses, or other underlying conditions.
Symptoms of Bell’s Palsy
The symptoms of Bell’s Palsy often appear suddenly and may vary in severity from person to person. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Sudden weakness or one side of the face is paralysis.
- Drooping of the mouth or eyelid.
- Difficulty closing one eye.
- Loss of taste sensation.
- Excessive tearing or drooling.
- Difficulty speaking or eating.
- Pain or discomfort behind the ear or in the jaw.
Diagnosis of Bell’s Palsy
Clinical Examination:
Diagnosis of Bell’s Palsy is primarily based on clinical evaluation of symptoms, including facial drooping, difficulty closing the eye, and other signs of facial nerve dysfunction. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential for ruling out other potential causes of facial paralysis.
Tests and Procedures:
In some cases, additional tests such as electromyography (EMG), imaging studies (MRI or CT scan), and blood tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of nerve damage. These tests help differentiate Bell’s Palsy from other conditions that mimic its symptoms.
Treatment Options for Bell’s Palsy
Medications:
The primary treatment for Bell’s Palsy involves medications, may be prescribed by doctor, which help reduce inflammation and speed up recovery. It is necessary to consult with your medical doctor.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy techniques, including facial exercises, massage, and electrical stimulation, can help improve muscle strength, mobility, and coordination with people. These exercises focus on retraining the facial muscles and restoring normal function over time.
Stress Management:
Stress, Depression and anxiety can exacerbate symptoms of Bell’s Palsy and hinder the recovery process. Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce tension and promote overall well-being during treatment.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Certain home remedies and natural treatments may offer relief from Bell’s Palsy symptoms. These may include:
- Using warm compresses on the affected side of the face.
- Performing gentle facial exercises to improve muscle tone and mobility.
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to reduce stress and promote healing.
Importance of Exercises
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining muscle tone and preventing stiffness and contractures. It also helps stimulate blood flow to the affected area, which can facilitate healing and reduce inflammation.
Best Exercises for Bell’s Palsy Recovery
Some of the best exercises for Bell’s Palsy recovery include:
- Facial massage: Gently massaging the affected side of the face can help improve circulation, reduce tension, and promote relaxation of the facial muscles.
- Eye exercises: Practicing eye movements, such as blinking, squinting, and rolling the eyes, can help prevent dryness and maintain eye health.
- Lip stretching: Stretching the lips into various positions, such as smiling, puckering, and blowing kisses, can help improve muscle strength and coordination.
- Tongue exercises: Moving the tongue in different directions and pressing it against the roof of the mouth can help improve speech clarity and swallowing function.
Professional Help
Seeking professional help from healthcare providers such as neurologists, otolaryngologists, physical therapists, and psychologists is essential for the comprehensive management of Bell’s Palsy. These experts can offer specialized care, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing monitoring to optimize outcomes and quality of life.
FAQs
- What are the main causes of Bell’s Palsy?
Bell’s Palsy is commonly caused by viral infections, nerve inflammation, or a combination of both factors. Viruses such as herpes simplex and Epstein-Barr are often implicated in the development of the condition.
- How much time does it typically require to recuperate from Bell’s Palsy?
The recovery timeline for Bell’s Palsy varies from person to person and depends on factors such as the severity of symptoms, the effectiveness of treatment, and people health status. Most people experience gradual improvement over several weeks to months, with full recovery within six to twelve months in many cases.
- Can stress worsen Bell’s Palsy symptoms?
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate symptoms of Bell’s Palsy and interfere with the recovery process. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, stress reduction strategies, and emotional support can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Can Bell’s Palsy affect both sides of the face?
Bell’s Palsy typically affects only one side of the face, but in rare cases, it can involve both sides simultaneously (bilateral Bell’s Palsy). Bilateral Bell’s Palsy may present more severe symptoms and require comprehensive evaluation and management by healthcare professionals.
- Is Bell’s Palsy contagious?
Bell’s Palsy itself is not contagious, but the viral infections that may cause it, such as herpes simplex virus, can be transmitted from person to person through close contact.
Remember, You are not alone in this disease. The aims of this article to provide comprehensive detail about Bell’s Palsy, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and recommended exercises for recovery.